Types of Prediction Market: Real Money, Play Money, and Decentralized Systems
Types of Prediction Market describe how forecasting platforms are designed around different funding models, liquidity mechanisms, and settlement architectures. Instead of relying on opinions or expert commentary, these markets turn collective expectations into live prices by letting participants trade on the outcomes of future events.
At their core, prediction markets function as information engines. Prices rise and fall as new data emerges, beliefs shift, and probabilities are reassessed. Some markets operate with real capital, others use virtual currency for experimentation, while newer models rely on blockchain-based settlement to remove intermediaries and increase transparency.
In this article, we’ll break down how each type works, where they are most effective, and how users can evaluate them responsibly—along with practical tools they may later use, such as Bitget Wallet, to participate safely in on-chain prediction markets.
What Is a Prediction Market?
Prediction markets are platforms where participants trade event-based contracts whose prices represent collective expectations about future outcomes. Rather than asking what people say will happen, prediction markets reveal what participants are willing to back with capital or reputation.

Source: Thecoinzone.com
How Are Prediction Markets Commonly Categorized?
Prediction markets are typically grouped using three classification layers:
- Currency-based Prediction Market**:** real money vs play money
- Mechanism-based Prediction Market**:** continuous double auction (CDA) vs automated market maker (AMM)
- Architecture-based Prediction Market**:** centralized vs decentralized systems
| Classification | Core Feature | Typical Use Case |
| Currency-based Prediction Market | Real vs virtual funds | Incentives & compliance |
| Mechanism-based Prediction Market | CDA vs AMM | Liquidity management |
| Architecture-based Prediction Market | Centralized vs decentralized | Control & transparency |
These layers overlap — a single platform may combine real money trading with centralized control, or virtual currency with automated liquidity.
Read more: What Is a Prediction Market in Crypto and How Blockchain-Based Prediction Markets Work
1. Currency-Based Types: Real Money vs. Play Money
Currency-based classification answers a very practical question: what are participants actually staking—real money or virtual points? This choice determines how serious predictions tend to be, the platform’s regulatory constraints, and who the model is truly suitable for. For beginners, this is almost always the first layer to understand in order to avoid “entering the wrong arena.”
Real Money Prediction Markets
Real money prediction markets allow users to trade event contracts using actual capital. Every buy or sell decision carries clear financial risk.
This is why real money markets often generate sharper information signals—but in exchange, they must operate within stricter legal frameworks and typically limit participation.
Why Do Real Money Markets Produce Stronger Signals?
When participants have real “skin in the game,” incorrect predictions do not merely cost points—they cost money. This forces traders to think more carefully, analyze data more deeply, and manage risk more seriously. Instead of guessing based on intuition, they must assess probabilities, weigh new information, and react with discipline.
Mini Case Study: Iowa Electronic Markets (IEM)
If IEM is mentioned, this is the point where it should become a concrete example rather than a name drop.
- How it works (conceptually): IEM operates small-scale event contracts focused on academic research; contract prices reflect collective expectations about future outcomes.
- Why it is often considered accurate: it combines real money (albeit small stakes), long-term empirical data, and a participant base motivated by serious analysis.
- Key limitation: it is not open to the general public, so it does not fully reflect mass-market behavior or retail user dynamics.
Source: iem.com
Play Money Prediction Markets
Play money prediction markets use virtual points or tokens instead of real funds. As a result, they are well suited for learning, experimentation, and internal forecasting—especially in regions or contexts where real money prediction markets are not permitted.
How Do Virtual Currencies Still Motivate Forecasting?
Even without direct financial risk, play money platforms can still encourage meaningful participation through system design:
- Providing an initial balance of virtual points
- Tracking performance via leaderboards and reputation scores
- Linking privileges, visibility, or status to forecasting performance
Clear trade-off: these markets are accessible and beginner-friendly, but accuracy can fluctuate because “losing” does not carry the same psychological pressure as losing real money.
2. Mechanism-Based Types: CDA vs. AMM (LMSR)
If the currency layer explains what is being staked, the mechanism layer explains how prices are formed and how trades are executed. CDA relies on order books and real counterparties; AMMs provide continuous liquidity through algorithms (often LMSR-based). This layer directly shapes liquidity and trading experience.
Continuous Double Auction (CDA / Order Book)
CDA is the familiar trading model used in traditional financial markets:
- Users place buy and sell orders
- Orders match when prices meet
- Prices move according to real-time supply and demand
Strength: transparent price discovery and efficiency in active markets.
Weakness: prone to freezing in niche topics where order books are thin and spreads are wide.
Automated Market Maker (AMM) + LMSR
AMMs were introduced to solve one of prediction markets’ biggest weaknesses: a lack of simultaneous participants. Instead of waiting for a counterparty, the system itself provides quotes.
What Does an AMM Actually Solve?
- Orders are always executable
- Small markets remain functional
- Prices adjust immediately after each trade
How Does LMSR Work? (High-Level)
In many prediction markets, AMMs rely on LMSR-style logic:
- Increased buying pressure → higher implied probability
- Increased selling pressure → lower implied probability
- Inventory risk is absorbed by the algorithm/market maker within predefined bounds
| Criterion | CDA (Order Book) | AMM (Often LMSR-Based) |
| Liquidity source | Traders | Algorithmic market maker |
| Execution certainty | Not guaranteed | Always available |
| Best suited for | High-volume markets | Niche or long-tail markets |
| Main drawback | Slippage, thin books | Price impact, maker risk |
Important note: AMM is a trading mechanism, not a currency classification. An AMM can operate with either real money or play money.
3. Architecture-Based Types: Centralized vs. Decentralized
The architecture layer answers a core question: who controls assets, rules, and outcome settlement? Centralized models rely on an operator; decentralized models rely on smart contracts and oracles. This layer determines trust assumptions and technical risk.
Centralized Prediction Markets
- The operator defines rules and handles settlement
- Users typically trade through accounts (sometimes with KYC)
- Custody and payouts are managed by the platform
Strength: clear governance and faster dispute resolution.
Risk: users must trust an intermediary.
Decentralized Prediction Markets (Smart Contracts + Oracles)
- Trades and payouts are executed by smart contracts
- Users retain custody and connect wallets directly
- Outcomes depend on oracles and/or governance mechanisms
Strength: transparency and reduced reliance on a single authority.
Risks: oracle manipulation, outcome disputes, and smart contract vulnerabilities.
What Makes Blockchain-Based Prediction Markets Different?
Blockchain-based prediction markets operate without a central operator. Instead, smart contracts handle trade execution, settlement, and payouts automatically.

How Does Decentralization Affect Trust and Control?
Decentralized systems remove intermediaries:
- Trades are settled on-chain
- Rules are enforced by code
- Users retain custody of funds
This design reduces reliance on centralized oversight and increases transparency, particularly for global participants.
What Risks Exist in Decentralized Prediction Markets?
Decentralization introduces new challenges:
- Oracle manipulation: incorrect outcome reporting
- Governance disputes: unclear resolution mechanisms
- Ethical concerns: unrestricted market creation
Because decentralized prediction markets are typically permissionless, anyone can create a market without prior approval or moderation. This openness can lead to ethically sensitive or controversial markets, unclear boundaries around acceptable topics, and disputes over how outcomes should be defined or resolved—issues that centralized platforms usually control through curation and rules.
Early platforms such as Augur made these risks visible in practice, as its fully open market design allowed controversial markets to be listed, highlighting the ethical and governance challenges inherent in permissionless forecasting systems.
Are Prediction Markets the Same as Gambling?
Prediction markets are often labeled as gambling because both involve placing money on uncertain outcomes. However, this comparison overlooks fundamental differences in purpose, pricing logic, and participant behavior. Understanding this distinction is essential for users evaluating different Types of Prediction Market responsibly.
At a structural level, prediction markets are designed to aggregate information. Prices move as participants respond to data, news, and probabilities, turning collective beliefs into measurable signals. Gambling platforms, by contrast, are built primarily for entertainment, with odds set by an operator rather than discovered through open trading.
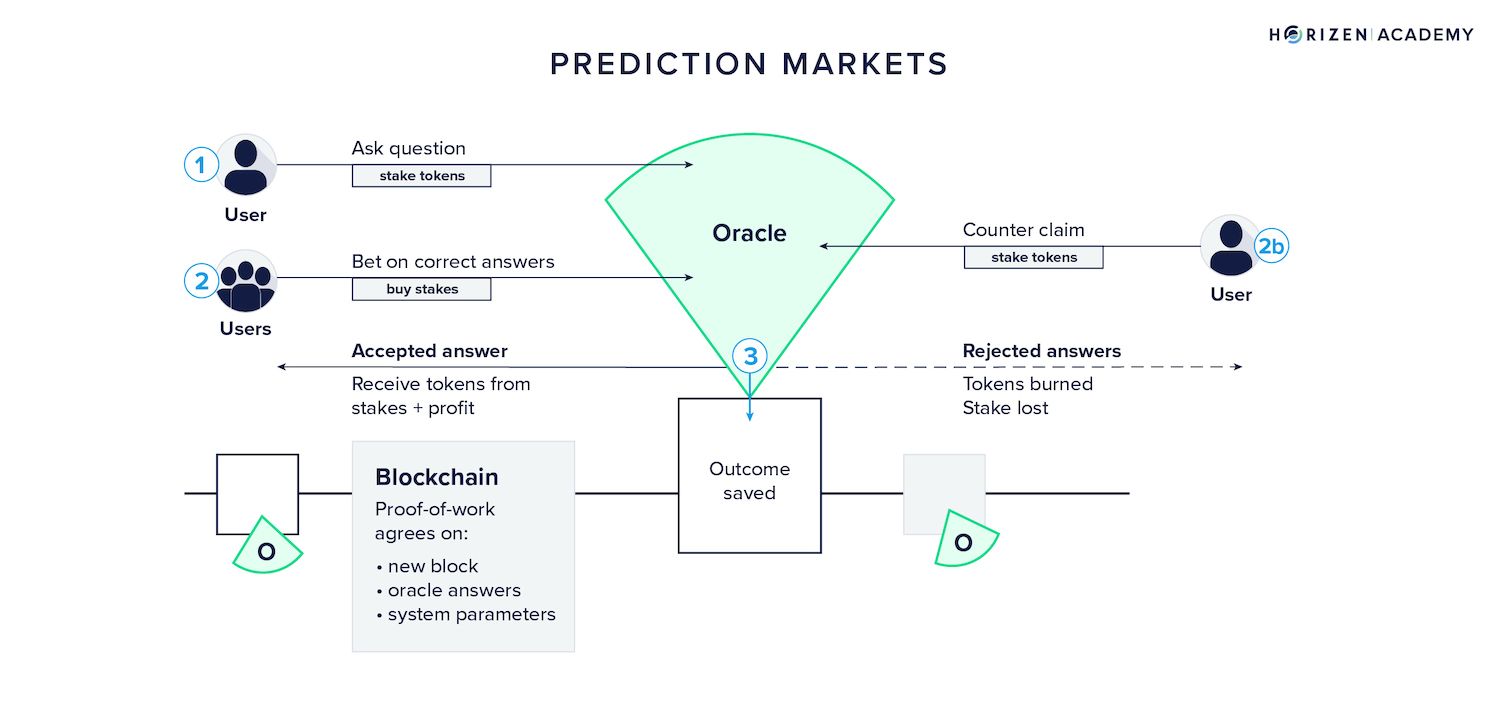
Source: Horizen
What Separates Prediction Markets from Traditional Gambling?
| Aspect | Prediction Markets | Gambling |
| Primary driver | Information, analysis, and belief | Randomness and chance |
| Pricing mechanism | Market-derived probabilities | House-set odds |
| Participant role | Active forecasting and trading | Passive wagering |
| Objective | Signal discovery and forecasting | Entertainment and payout |
In prediction markets, participants influence prices directly through trades, meaning outcomes reflect crowd intelligence rather than fixed probabilities. This is why economists and researchers often view prediction markets as analytical tools rather than games of chance.
Read more: Is Prediction Market Gambling: Sports Betting or Financial Forecasting?
Why Do Regulators Still Debate This Classification?
Despite these differences, regulatory classification remains contested. The debate largely stems from functional overlap, especially as prediction markets expand beyond academic and political use cases.
Key points driving regulatory uncertainty include:
- Sports-related contracts that closely resemble traditional betting markets
- Broad public participation, increasing concerns about consumer protection
- Jurisdictional differences, where financial regulators and gambling authorities apply conflicting frameworks
As prediction markets increasingly cover sports, pop culture, and crypto price outcomes, regulators continue to reassess where forecasting ends and gambling begins. This evolving landscape explains why legality and access vary significantly across regions.
How Should Beginners Evaluate Different Types of Prediction Market?
Choosing among the Types of Prediction Market depends less on potential returns and more on intent, experience level, and risk tolerance. Not all market types are suitable for every user.
For newcomers, understanding why a market exists is often more important than predicting outcomes correctly.

Source: ESPN
Which Type Suits Educational Users Best?
Play money prediction markets are often the most appropriate starting point. Because they operate without real financial risk, users can:
- Learn how probability pricing works
- Observe how information affects market sentiment
- Experiment without capital exposure
These environments prioritize learning and engagement over accuracy, making them ideal for first-time participants.
Which Type Is Better for Serious Forecasters?
Real money prediction markets are designed for participants who value accuracy and accountability. Financial incentives encourage deeper research and disciplined decision-making. However, users must also be aware of:
- Regulatory limitations
- Jurisdiction-specific access rules
- The psychological impact of financial risk
These markets are best suited for users who understand both forecasting mechanics and compliance considerations.
When Should Users Approach Decentralized Markets Cautiously?
Decentralized prediction markets introduce additional layers of complexity. While they offer transparency and self-custody, they also demand higher technical competence.
Users should proceed cautiously if they are unfamiliar with:
- Smart contract behavior and risks
- Oracle-based outcome resolution
- Self-custody security practices
For experienced users, decentralized markets offer autonomy and censorship resistance. For beginners, however, the learning curve can be steep.
How Can Users Safely Explore Prediction Markets Using Bitget Wallet?
Types of Prediction Market increasingly include on-chain platforms that require users to interact directly with decentralized applications. For this reason, choosing the right self-custody tool matters as much as understanding market mechanics.
How Does Bitget Wallet Support On-Chain Participation Safely?
Bitget Wallet is a non-custodial, cross-chain wallet designed for users who want direct access to decentralized applications without giving up control of their assets.
Key safety and usability features include:
- Self-custody: private keys remain with the user
- Wallet-based signing: transactions require explicit approval
- Cross-chain access: support across major ecosystems
- Integrated Web3 browser: discover and connect to prediction market dApps directly
This structure allows users to interact with smart contracts while maintaining transparency over every transaction.
How to Participate in Prediction Markets with Bitget Wallet?
Using a non-custodial wallet is one of the safest ways to explore decentralized prediction markets, especially when outcomes and settlements are handled on-chain. Bitget Wallet enables users to connect directly to prediction market dApps, approve transactions transparently, and retain full control over their assets at every step.
Below is a practical, step-by-step flow for getting started.
Step 1: Set up a non-custodial wallet
Begin by creating a Bitget Wallet and completing the initial security setup. This ensures you, not a third party, control your private keys and approvals.
- Create a new Bitget Wallet
- Securely back up your recovery phrases offline
- Enable basic security settings such as passcodes or biometric access
Step 2: Fund the wallet
Before interacting with any prediction market, add a small amount of supported assets.
- Use stablecoins or other supported tokens
- Start with small test amounts to minimize risk during early interactions
Step 3: Access prediction market dApps
Bitget Wallet includes an integrated Web3 browser, allowing users to reach on-chain prediction markets without relying on external tools.
- Open the Web3 browser in the Discover section
- Search for a prediction market platform by name or enter its direct URL
- Once on the platform, connect your wallet directly to access available markets
Step 4: Interact with prediction contracts
After connecting, users can begin interacting with prediction contracts on-chain.
- Select a market based on the event or outcome you want to forecast
- Review contract terms, settlement conditions, and timelines carefully
- Approve and sign transactions directly through the wallet interface
Step 5: Monitor outcomes on-chain
Once a position is open, transparency becomes critical.
- Track your positions and settlement status directly on-chain
- Verify outcomes using smart contract data
- Avoid relying solely on centralized dashboards or third-party summaries
With just a few simple steps, you can securely manage your assets and explore decentralized forecasting tools. Don’t hesitate — start your beginner-friendly, non-custodial Web3 journey with Bitget Wallet.
Conclusion
Types of Prediction Market highlight how modern forecasting platforms are shaped by their funding models, trading mechanics, and underlying architecture. Real money markets sharpen accuracy through financial incentives, play money markets lower barriers for learning and experimentation, while decentralized systems shift control back to users through transparent, on-chain settlement.
As prediction markets increasingly move on-chain, the way users access them matters just as much as the markets themselves. A non-custodial, cross-chain wallet becomes essential for maintaining security, visibility, and autonomy. With self-custody by design, an integrated Web3 browser, and seamless access across ecosystems, Bitget Wallet gives users a practical gateway to explore decentralized prediction markets—without giving up control of their assets.
Download Bitget Wallet to trade, store, and explore Web3 forecasting tools seamlessly — built for beginners!
Sign up Bitget Wallet now - grab your $2 bonus!
FAQs
1. What Are the Main Types of Prediction Market?
The main Types of Prediction Market include real money markets, play money markets, and decentralized prediction markets. They differ by funding method, liquidity mechanism, and how contracts are settled.
2. How Do Real Money and Play Money Prediction Markets Differ?
Real money markets use financial capital to incentivize accuracy, while play money markets rely on virtual currency and reputation systems for engagement and learning.
3. Is Bitget Wallet Suitable for Interacting With Prediction Market dApps?
Yes. Bitget Wallet supports non-custodial access, wallet-based transaction signing, and cross-chain connectivity, making it suitable for interacting with decentralized prediction market applications.
4. Which Is More Suitable for Beginners: CDA or AMM—and Why?
AMM-based markets are generally more suitable for beginners because trades are always executable and liquidity is provided automatically. CDA markets require understanding order books and can be difficult to use in low-liquidity conditions.
5. Why Don’t the “Yes” and “No” Prices Always Add Up to Exactly 1?
In prediction markets, prices reflect trading demand and liquidity, not perfect probabilities. Fees, liquidity imbalances, and market mechanics (especially AMMs) can cause “Yes” and “No” prices to temporarily deviate from summing to 1.
Risk Disclosure
Please be aware that cryptocurrency trading involves high market risk. Bitget Wallet is not responsible for any trading losses incurred. Always perform your own research and trade responsibly.
- Is Prediction Market Legal: US Federal vs State Laws Explained2026-01-05 | 5 mins
- Prediction Market Risks: What Investors Should Know Before Getting Started2025-12-30 | 5 mins



















